Filter
Filter
서블릿 필터는 웹 응용 프로그램의 요청과 응답을 가로채어 전처리, 후처리를 위해 사용되는 자바 클래스이다.
Examples that have been identified for this design are:
- Authentication Filters
- Logging and Auditing Filters
- Image conversion Filters
- Data compression Filters
- Encryption Filters
- Tokenizing Filters
- Filters that trigger resource access events
- XSL/T filters
- Mime-type chain Filter
Filter Methods
package javax.servlet;
public interface Filter {
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException;
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
public void destroy();
}
- init: This method is called by the web container to indicate to a filter that it is being placed into service. It is passed a FilterConfig object, which the filter can use to obtain any initialization parameters.
- doFilter: This method is called by the container each time a request/response pair is passed through the chain due to a client request for a resource at the end of the chain. The FilterChain passed in to this method allows the Filter to pass on the request and response to the next entity in the chain.
- destroy: This method is called by the web container to indicate to a filter that it is being taken out of service.
The init method is invoked only once, at the time of filter instance creation by the web container, whereas the doFilter method is invoked for each request-response pair. The destroy method is invoked only once, when the filter is going out of service.
Filter Process
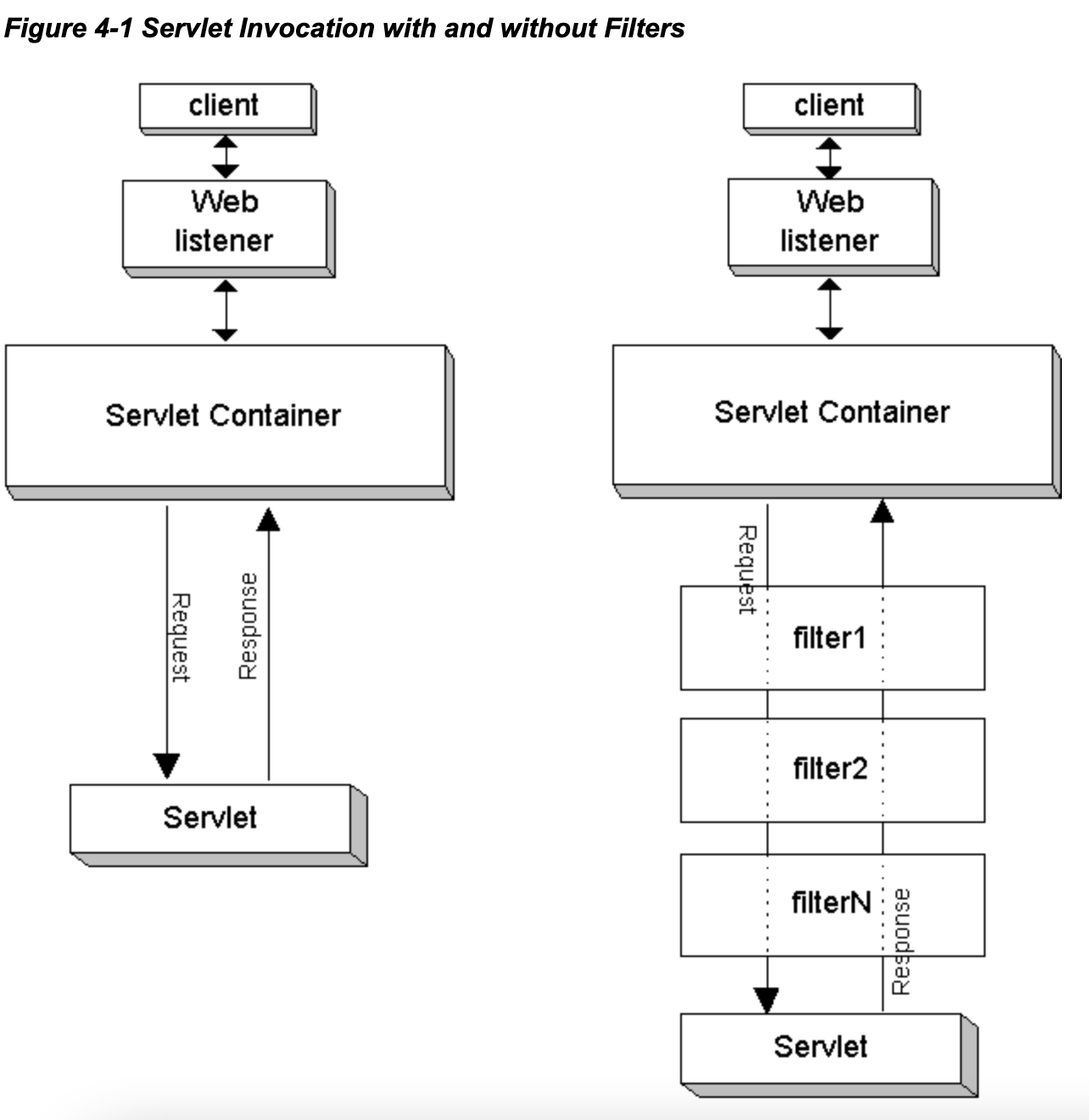
Can the filter be invoked twice?
A single instance filter in Spring can be called twice in certain circumstances.
- If a filter is mapped to a URL pattern that is included in the URL pattern of another filter, the filter will be called twice for a request that matches both URL patterns. For example, if filter A is mapped to the URL pattern "/example/" and filter B is mapped to the URL pattern "/example/subpath/", then a request to the URL "/example/subpath/test" will cause filter A to be called followed by filter B, both are single instance filter.
- Another scenario where a single instance filter can be called twice is when a request is forwarded to another servlet or JSP page using the RequestDispatcher. If a filter is mapped to a URL pattern that includes the URL of the page to which the request is forwarded, the filter will be called again when the request is processed by the forwarded page.
- It's also worth noting that, if the filter is marked as asyncSupported=true, it will be called twice, once for the main request and once for the async request.
In summary, a single instance filter in Spring can be called twice in certain circumstances such as:
- Case1. filter is mapped to a URL pattern that is included in the URL pattern of another filter
- Case2. when a request is forwarded to another servlet or JSP page using the RequestDispatcher
- Case3. if the filter is marked as asyncSupported=true.
마지막 summary 부분이 아주 중요하다. Filter 는 특정 상황에 두 번 호출될 수 있다는 것이다. 예를 들면, Spring Security 를 사용하는 경우 DispatcherServlet 까지 도달하기 전에 RequestDispatcher 에 의해서 다른 서블릿으로 dispatch 될때 Filter 가 두 번 실행될 수 있다.
이러한 문제를 스프링에서는 OncePerRequestFilter 을 상속 받아서 클래스를 구현하면 단 한 번만 처리되는 필터를 만들 수 있다.
Multiple Instance Filter
Filter 가 두 번이상 동작하기 위해서는 multiple instance filter 가 되어야 한다.
<filter>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.example.MyFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>filter-config-param</param-name>
<param-value>filter-config-value</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>filter-config-param2</param-name>
<param-value>filter-config-value2</param-value>
</init-param>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
<init-param>
<param-name>create-new-instance</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>myFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
create-new-instance 옵션이 true 이기 때문에 위 설정은 multiple instance filter 이다. 또한 async-supported 가 true 이기 때문에 이 설정으로 인해 필터는 두 번 호출될 수도 있다.
RequestDispatcher
RequestDispatcher is an interface provided by the Servlet API that is used to forward or include a request from one servlet to another resource such as a servlet, JSP file, or HTML file.
public interface RequestDispatcher {
public void forward(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException;
public void include(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException;
}
forward()method is used to forward the request and the response from the current servlet to another resource. The resource can be a servlet, JSP file, or HTML file.include()method is used to include the content of another resource in the response. The resource can be a servlet, JSP file, or HTML file.
GenericFilterBean
GenericFilterBean is a Spring Framework class that is a subclass of Object and provides a convenient base class for filter implementations that do not wish to implement the Filter interface. It is a convenience class that allows filter developers to only implement the doFilter() method and the init() and destroy() methods if needed.
public abstract class GenericFilterBean implements Filter, BeanNameAware, EnvironmentAware,
EnvironmentCapable, ServletContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
// ...
}
GenericFilterBean provides the following benefits:
- It implements the Filter interface, which makes it easy to use with the standard Servlet API.
- It automatically creates a FilterConfig object and makes it available through the
getFilterConfig()method, so that filter developers don't need to implement this themselves. - It automatically calls the
init()anddestroy()methods at the appropriate times, so that filter developers don't need to worry about this. - It automatically calls the
doFilter()method, passing the request and response objects and the filter chain, so that filter developers don't need to worry about this either. - By extending GenericFilterBean, the developer can focus on the logic of doFilter method, and also it provides a way to get the FilterConfig object, and also it provides a way to handle the initialization and destruction of the filter.
OncePerRequestFilter
OncePerRequestFilter is a Spring Framework class that is a subclass of GenericFilterBean and provides a convenient base class for filter implementations that should only be executed once per request.
Filter is an interface provided by the Servlet API, which all filter classes must implement.
The main difference between OncePerRequestFilter and Filter is that OncePerRequestFilter guarantees that its doFilterInternal() method will only be called once per request, whereas a Filter implementation does not have this guarantee. With a Filter implementation, it is possible for the doFilter() method to be called multiple times for the same request, depending on how the filter is configured and how many times the filter is mapped to a particular URL pattern or servlet.
OncePerRequestFilter also provides a shouldNotFilter() method which can be overridden to filter out certain requests, it provides a getAlreadyFilteredAttributeName() method which can be overridden to customize the name of the request attribute that is used to track whether a request has already been filtered, and it provides a way to handle the initialization and destruction of the filter.
On the other hand, Filter interface provides a way to handle the request before it reaches to the target servlet or resource and also after the target servlet or resource is executed.
In summary, OncePerRequestFilter is a more convenient option if you want to ensure that your filter is only executed once per request, and you also want to filter out certain requests and handle the initialization and destruction of the filter, while Filter is a more general solution that provides a way to handle the request before it reaches to the target servlet or resource and also after the target servlet or resource is executed.
LoggingFilter
OncePerRequestFilter 를 구현한 LoggingFilter 예시이다. doInterInternal 에서는 전처리와 후처리를 한다.
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.slf4j.MDC;
import org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter;
public class LoggingFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(LoggingFilter.class);
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// Add log context to MDC
MDC.put("requestId", request.getHeader("X-Request-Id"));
try {
// Log request details - pre-processing
LOGGER.info("Received {} request for {}", request.getMethod(), request.getRequestURI());
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
// Log response details - post-processing
LOGGER.info("Sent {} response for {} in {} ms", response.getStatus(), request.getRequestURI(), System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
} finally {
// Clear log context from MDC
MDC.clear();
}
}
}